Search-Augmented Large Language Models: RAG Patterns That Improve Accuracy
Large language models (LLMs) are powerful, but they’re not perfect. Ask them a question about a recent regulation, a product update, or a medical guideline, and they’ll often guess - confidently - instead of knowing. That’s not just frustrating; it’s risky in business, healthcare, or legal settings. The fix isn’t more training data or bigger models. It’s RAG - Retrieval-Augmented Generation. This isn’t a buzzword. It’s the reason companies are finally seeing real accuracy gains from AI.
What RAG Actually Does (And Why It Matters)
RAG isn’t magic. It’s a simple idea: before answering, ask the model to look up what’s real. Instead of relying only on what it learned during training - which could be years old - RAG pulls in live, relevant documents from your own data. Think customer emails, policy manuals, product specs, or legal briefs. The model reads those first, then writes its answer based on what it found. The result? Answers grounded in your facts, not hallucinated guesses. Google and Microsoft’s internal tests show RAG boosts factual accuracy from 45-68% to 82-94% on real-world queries. In one healthcare case, error rates dropped from 38% to 11% when RAG was added to a clinical decision tool. That’s not incremental. That’s life-changing.The Three Core Pieces of RAG
Every RAG system runs on three parts:- Pre-processing and indexing: Your documents get split into chunks - usually 256 to 512 tokens long - and turned into numerical vectors. This lets machines understand meaning, not just keywords.
- Retrieval: When a user asks a question, the system searches those vectors to find the most similar chunks. It doesn’t just look for matching words; it finds contextually related ideas. Vector databases like Pinecone or Milvus handle this at scale.
- Grounded generation: The top 3-5 retrieved chunks are fed into the LLM along with the original question. The model then writes a response using that context as its source.
Why RAG Beats Fine-Tuning for Most Businesses
You might think: “Why not just fine-tune the model on our documents?” That sounds smart - until you realize the cost. Retraining a large model on 10,000 documents can cost $85,000 and take weeks. And if your documents change next month? You start over. RAG costs about 6-8 times less. A typical enterprise implementation runs around $12,500. More importantly, it updates instantly. Add a new policy PDF? Index it. Next time someone asks, the model sees it. No retraining. No downtime. That’s why 78% of companies using generative AI in 2023 chose RAG over fine-tuning, according to Gartner.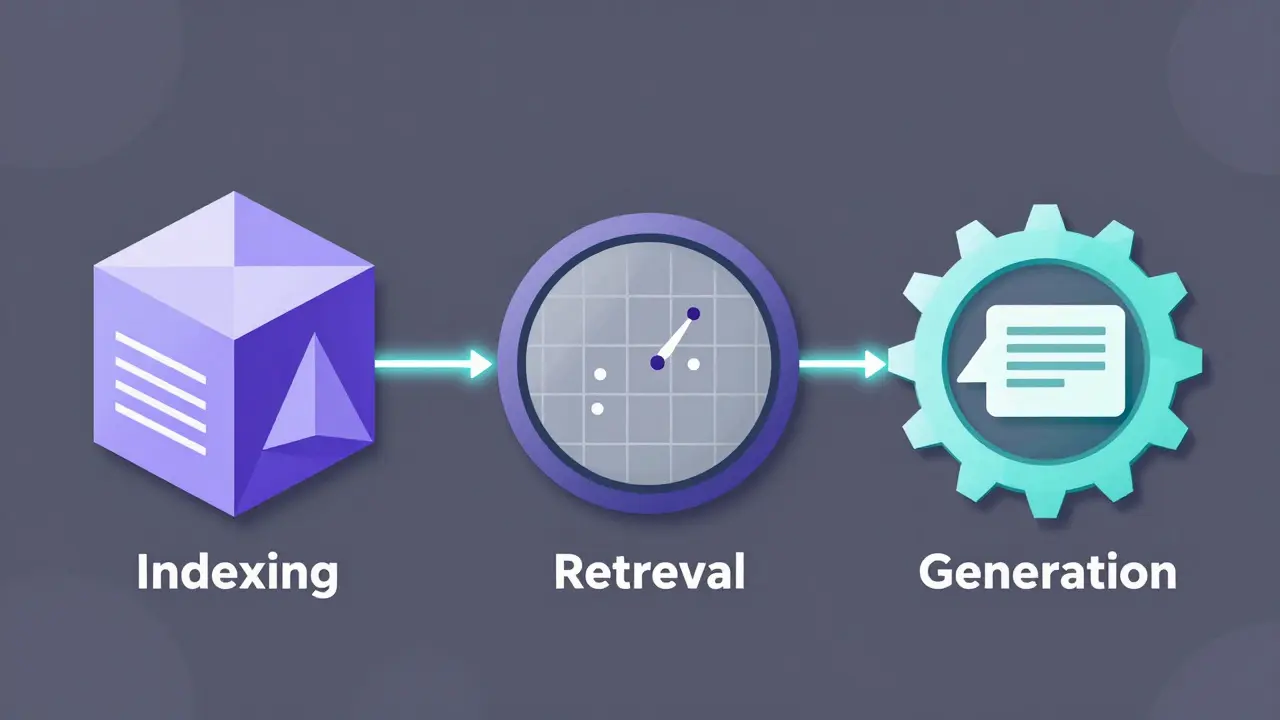
Advanced RAG Patterns That Actually Boost Accuracy
Basic RAG helps. But the best systems use smarter patterns. Here are the top three:- Hybrid search: Combine keyword search (like BM25) with vector search. Keyword search finds exact matches. Vector search finds meaning. Use 30-40% keyword, 60-70% vector. Google’s tests show this improves recall by 25%.
- Query expansion: When someone types, “What’s our refund policy for defective laptops?” the system might expand it to include “return policy,” “warranty claim,” “defective hardware.” This catches more relevant docs. Accuracy jumps 27%.
- Re-ranking: After retrieval, run the top results through a second model - like Cohere Rerank - to sort them by true relevance. This boosts the quality of the top 3 results by 22%.
Where RAG Falls Short - And How to Fix It
RAG isn’t perfect. It has blind spots. First, garbage in, garbage out. If your document chunks are too big, the model misses key details. If they’re too small, it loses context. Legal documents, for example, need sentence-window chunking - where each chunk includes the sentence before and after - to preserve meaning. One bank saw accuracy drop 33% until they fixed their chunking. Second, multi-hop questions break standard RAG. “What’s the average turnaround time for claims processed by the Chicago team after the July policy update?” That requires linking two documents. Standard RAG gets it right only 54% of the time. The fix? Tree of Thoughts - a pattern that explores multiple reasoning paths before answering. It bumps accuracy to 79%. Third, bad queries hurt. If someone types, “Tell me about the thing,” RAG can’t help. That’s why query transformation matters. Systems now auto-correct vague questions before retrieval. Without it, accuracy can drop 15-20%.
Real-World Results From Companies Using RAG
A Fortune 500 bank reduced incorrect loan policy responses from 32% to 9% after six months of tuning RAG. A telecom company cut customer service errors by 47% using RAG in their chatbot. In healthcare, one hospital system improved compliance with FDA guidelines by 41% because their AI now pulled from the latest internal audit logs. G2 reviews show 78% of users list “accuracy improvement” as the top benefit. But 65% also say setup was too complex. That’s the trade-off. RAG works - but it’s not plug-and-play. You need to tune chunk sizes, test retrieval thresholds, and monitor for irrelevant results.What You Need to Get Started
You don’t need a PhD. But you do need:- A source of truth: PDFs, databases, or internal wikis with up-to-date info.
- A vector database: Pinecone, Milvus, or even Azure AI Search if you’re on Microsoft.
- A framework: LangChain or LlamaIndex for open-source; Vertex AI Search or Azure AI Search for managed.
- Time: Most enterprise deployments take 8-12 weeks. The hardest part? Prepping your documents.
The Future of RAG
By 2025, 92% of enterprise LLM apps will use RAG, according to Forrester. The next wave? Recursive retrieval - where the model asks follow-up questions to itself to dig deeper. Or multi-modal RAG, where it pulls from images, spreadsheets, and text together. The big shift? RAG won’t stay an add-on. By 2026, it’ll be built into the core of every major LLM. But until then, if you want accurate, trustworthy AI - especially in regulated industries - RAG isn’t optional. It’s the only path that works.What is RAG in AI?
RAG stands for Retrieval-Augmented Generation. It’s a technique that improves large language models by first searching for relevant, real-world documents (like internal reports or policy files), then using that information to generate answers. This prevents the model from making up facts based only on its training data.
How much does RAG improve accuracy?
RAG typically improves factual accuracy from 45-68% (for base LLMs) to 82-94% in enterprise settings. In healthcare and financial services, accuracy gains of 35-60% are common. Some advanced RAG patterns, like Tree of Thoughts, push accuracy to 79% on complex reasoning tasks.
Is RAG better than fine-tuning?
For most businesses, yes. Fine-tuning costs 6-8 times more ($85,000 vs. $12,500) and requires retraining every time your data changes. RAG updates instantly - just add new documents. It’s faster, cheaper, and better for dynamic information like regulations or product updates.
What are the biggest challenges with RAG?
The top three are: 1) Poor document chunking - too big or too small chunks hurt accuracy; 2) Irrelevant retrieval - if the search pulls wrong docs, the answer gets worse; 3) Complex queries - multi-hop questions (needing info from multiple sources) break basic RAG. Solutions include hybrid search, re-ranking, and advanced patterns like Self-RAG or Tree of Thoughts.
Do I need a vector database for RAG?
Yes. Vector databases (like Pinecone, Milvus, or FAISS) are essential for fast, accurate semantic search. They turn text into numerical vectors so the system can find documents by meaning, not just keywords. Small setups need 8-16GB RAM; enterprise systems with millions of documents need 64GB+ and GPU acceleration.
Can RAG handle confidential data?
Yes, but you must design it carefully. RAG can keep data private because it only retrieves from your internal sources - no data leaves your system. For GDPR or HIPAA compliance, you’ll need data masking, access controls, and audit logs for retrieval. This adds 23-37% extra development effort, but it’s manageable.
What tools are best for building RAG?
For open-source: LangChain and LlamaIndex are the most popular. For managed cloud services: Google’s Vertex AI Search, Microsoft’s Azure AI Search, and AWS Knowledge Base for Bedrock. Start with a managed service if you’re new - it reduces setup time from months to weeks.
How long does RAG implementation take?
Most enterprise deployments take 8-12 weeks. The longest phase is document preparation - chunking, cleaning, and indexing your data. That takes 35-40% of total effort. Testing and tuning retrieval parameters can take another 3-6 weeks. Expect to spend 3-6 months learning the tools if you’re new to vector databases.
- Jan, 20 2026
- Collin Pace
- 7
- Permalink
- Tags:
- RAG patterns
- retrieval-augmented generation
- LLM accuracy
- search-augmented AI
- RAG implementation
Written by Collin Pace
View all posts by: Collin Pace